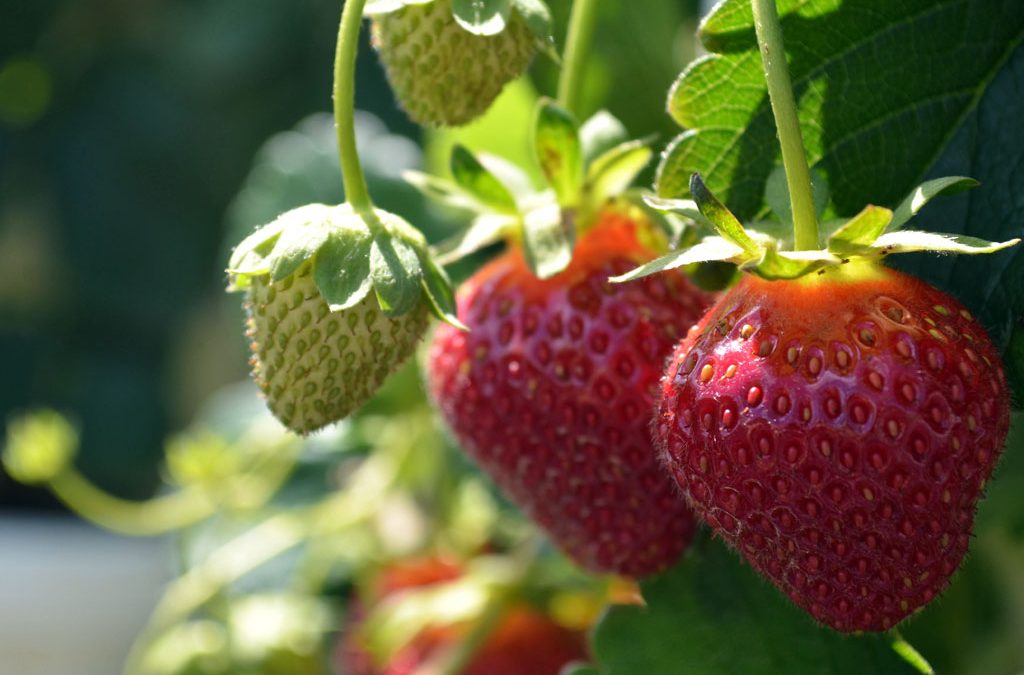

The Strawberry Plant
Strawberry growth will start from the crown. Strawberry crowns are perennial (live year after year) but their roots are annual. Each year the strawberry plant sends out new roots from the crown. This means that after a few years the roots get higher and higher up on the crown. This is why older plants need to have soil added to them.
Strawberry Growth And Development
The time required to go from flowers to mature fruit depends on the air and soil temperatures; the higher the temperature the faster it grows. Growth slows down as the temperature decreases. Temperatures lower than 40° Fahrenheit will cause the plant and the fruit to go stop growing. Water is very important to the strawberry during fruit formation and throughout fruit development and maturity. If there is not enough water it will show in the poor fruit quality. Water needed to “plump up” the berry will go out of the berry and into the leaves and crown to keep the plant alive under hot and dry conditions. The fruits shrivel and probably will never regain their full potential size. It is very important to have plenty of water during the period of final fruit swell just before the berries get ripe. Pick off the blossoms during the first year so the plant puts all of its energy into its own growth instead of fruit production. Removing the flowers encourages more runners to form.
Winter Care
A winter mulch should be applied to your strawberries after the first hard frost. A light frost will not harm the plants, but they should be protected from hard freezes. If the mulch is applied too early, the plants will not become as winter hardy as they should. They could suffer during the coldest parts of the winter if they do not have a mulch cover. If applied too late, the plants will have already experienced damage to their crowns and nest year’s fruit buds; resulting in a poorer crop. When new leaves start to develop in the spring, fork off the winter mulch and place it between the rows in the pathways. Winter mulch will cover over the plants themselves. Clear off the mulch each spring or it will delay the growth. The purpose of a winter mulch is to protect plants from cold and against soil heaving due to changing temperatures. The mulch should be at least 4 inches thick. Snow acts as a natural winter mulch that will insulate plants from the cold. Because snowfall is unreliable, it is better to use straw.
Berry Development
The second spring after planting strawberry plants will flower again. Bees visit the flowers and spread pollen from flower to flower. Strawberry flowers have many female flower parts. Pollen must be placed on each one for a seed to develop. The eveloping seeds release plant hormones that cause the berry to swell and become sweet and tasty. If the seeds are removed from one side of an immature strawberry that side of the berry will stop growing. Under normal conditions it will take from 30 to 45 days from flowering to harvest.
Harvest and Storage
Strawberries will turn bright red when they are ripe and ready to be harvested. Carefully pick the berry by pinching the stem between your thumb and forefinger and pull with a twisting motion. Leave the stem on the fruit. Don’t wash the fruit until you are ready to eat it. Strawberries can be stored for a few days to a week in the refrigerator. When you are ready to eat them, wash the strawberries in cold running water. Strawberries freeze well for eating later, too! Prepare them like you would for eating, but place them in bags in the freezer. If you want to be able to remove only a few berries from the freezer at a time, freeze the berries on waxed paper on a tray or cookie sheet and them put the frozen berries in bags.

Growing Strawberries with the EzGro System

Caring For Your Strawberry Plants on Arrival
Trackbacks and pingbacks
No trackback or pingback available for this article.
Articles
Featured
-
 Rainwater Pressure Tank SystemRegular Price $449.00
Rainwater Pressure Tank SystemRegular Price $449.00 -
 Submersible Thermoplastic Sump Pump 1/2 HPRegular Price $269.00
Submersible Thermoplastic Sump Pump 1/2 HPRegular Price $269.00 -
 Patio Garden Recharge KitRegular Price $49.00
Patio Garden Recharge KitRegular Price $49.00 -
 Cold Pressed Neem OilRegular Price $29.92 – $38.71
Cold Pressed Neem OilRegular Price $29.92 – $38.71 -
 EzGro Patio GardenRegular Price $389.99 – $399.99
EzGro Patio GardenRegular Price $389.99 – $399.99 -
 Thermoplastic Irrigation Pump 1 HPRegular Price $469.99
Thermoplastic Irrigation Pump 1 HPRegular Price $469.99 -
 EzGro Quad Pot 50 PackRegular Price $499.90
EzGro Quad Pot 50 PackRegular Price $499.90 -
 Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00
Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00 -
 Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95
Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95 -
 Five Tower Strawberry GardenRegular Price $2,799.00
Five Tower Strawberry GardenRegular Price $2,799.00









Leave a reply