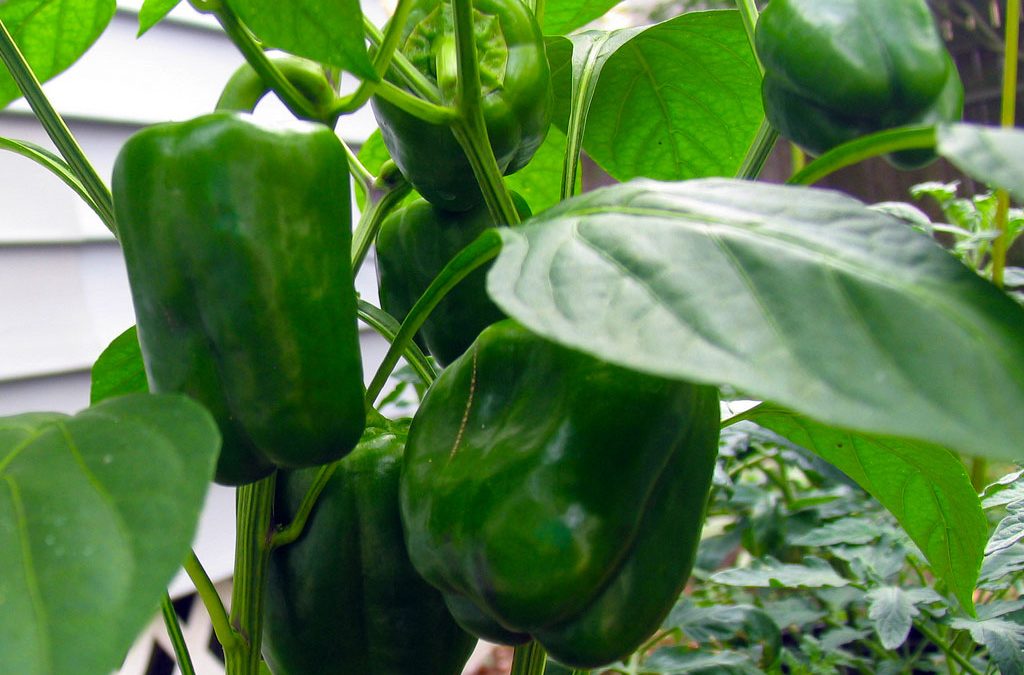

Calcium in Plants
Calcium uptake and mobilityCalcium uptake by the plant is passive and does not require energy input. Calcium mobility in the plant takes places mainly in the xylem, together with water. Therefore calcium uptake is directly related to the plant transpiration rate. Conditions of high humidity, cold and a low transpiration rates may result in calcium deficiency. Salinity buildup might also cause calcium deficiency because it decreases the water uptake by the plant. Since calcium mobility in plants is limited, calcium deficiency will appear in younger leaves (die back or burns) and in fruits (blossom end rot, bitter pit), because they have a very low transpiration rate. Therefore, it is necessary to have a constant supply of calcium for continued growth.
Roles of calcium in plantsCalcium is an essential plant nutrient. It has many roles:
Factors affecting calcium availabilityCalcium forms insoluble compounds with other elements in soil, such as phosphorous. Calcium that is in the form of an insoluble compound is not available to plants. Since calcium is a positively charged ion, it is adsorbed in the soil to the surface of clay and organic particles which are negatively charged. Positively charged ions adsorbed to soil particles are termed “exchangeable ions” because they can be exchanged by other ions present in the soil solution. Soil analysis determines the level of exchangeable calcium ions, and not the total calcium in soil, because the exchangeable calcium is the form which is available to the plant. Several factors in the soil analysis can help in assessing the availability of calcium to plants:
Additional reactions of calcium in soilCalcium-phosphorous precipitation – when free calcium accumulates in the soil solution (e.g. when soil pH is high), calcium tend to form insoluble compounds with phosphorous. Consequently, phosphorous availability is also significantly decreased. Calcium stabilizes soil structure – the calcium that is adsorbed to soil particles helps in stabilizing the soil structure. Adsorbed sodium might cause the soil to crack when dry and swell up when wet. Calcium replaces the adsorbed sodium and prevents damages to soil structure.
Calcium deficiencyCalcium deficiency is usually caused due to low calcium availability or due to water stress which results in low transpiration rates. The symptoms of calcium deficiency include curling of young leaves or shoots scorching or spotting on young leaves, poor growth, leaf tip burnes, stunted roots, and damage to fruit. |
 |
 |

Hydroponic Nutrients

EC vs TDS

How Plants Uptake Nutrients

pH Measurement

Types of Water in a Hydroponic System
Trackbacks and pingbacks
No trackback or pingback available for this article.
Articles
Featured
-
 EzGro Quad Pot 50 PackRegular Price $499.90
EzGro Quad Pot 50 PackRegular Price $499.90 -
 Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95
Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95 -
 EzGro Precision Micro TrimmerRegular Price $11.99
EzGro Precision Micro TrimmerRegular Price $11.99 -
 Patio Garden Recharge KitRegular Price $49.00
Patio Garden Recharge KitRegular Price $49.00 -
 Outdoor 3 Outlet Smart Plug TimerRegular Price $39.99
Outdoor 3 Outlet Smart Plug TimerRegular Price $39.99 -
 Five Tower Strawberry GardenRegular Price $2,799.00
Five Tower Strawberry GardenRegular Price $2,799.00 -
 Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00
Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00 -
 5000 Watt 48 Volt Power InverterRegular Price $899.00
5000 Watt 48 Volt Power InverterRegular Price $899.00 -
 Chemilizer InjectorRegular Price $349.99
Chemilizer InjectorRegular Price $349.99 -
 Vegetable Formula single dose SetRegular Price $29.99
Vegetable Formula single dose SetRegular Price $29.99









Leave a reply