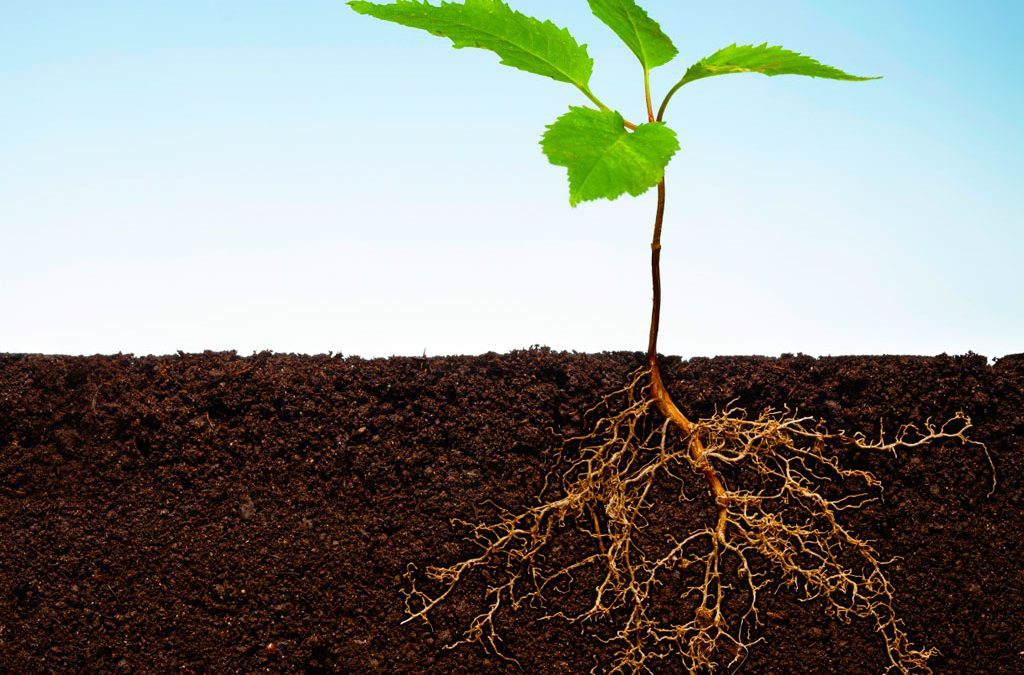

Aggregate Hydroponics (Agroponics)
In aggregate hydroponic systems, a solid, inert medium provides support for the plants. As in liquid systems, the nutrient solution is delivered directly to the plant roots. Agroponic systems may be either open or closed, depending on whether surplus amounts of the solution are to be recovered and reused. Open systems do not recycle the nutrient solutions; closed systems do.
In most open hydroponic systems, excess nutrient solution is recovered; however the surplus is not recycled to the plants, but is disposed of in evaporation ponds or used to irrigate adjacent landscape plantings or wind breaks. Because the nutrient solutions are not recycled, such open systems are less sensitive to the composition of the medium used or to the salinity of the water. These factors have generated experiments with a wide range of growing media and the development of more cost-efficient designs for containing them.
There are numerous types of media used in Agroponic systems. They include coconut coir, perlite, or a combination of both. Other media such as peat, vermiculite, rockwool, sand, sawdust, are also common.
For growing row crops such as tomato, cucumber, and pepper, the two most popular artificial growing media are coconut coir and perlite. Both of these media can be used in either closed or open systems (gravel is not recommended as an aggregate in either system). Both media are lightweight when dry, easily handled and easier to steam-sterilize than many other types of aggregate materials. Both can be incorporated as a soil amendment after crops have been grown in it.

Hydroponic Nutrients

EC vs TDS

Organic Does Not Mean “No Pesticides”

How Plants Uptake Nutrients

What is Aquaponics
Trackbacks and pingbacks
No trackback or pingback available for this article.
0 comments
Leave a reply Delete Message
Articles
Featured
-
 Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95
Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 5 PackRegular Price $69.95 -
 EzGro Patio GardenRegular Price $389.99 – $399.99
EzGro Patio GardenRegular Price $389.99 – $399.99 -
 Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00
Tri-Helix Solar WindmillRegular Price $4,399.00 -
 5000 Watt 48 Volt Power InverterRegular Price $899.00
5000 Watt 48 Volt Power InverterRegular Price $899.00 -
 EzGro Precision Micro TrimmerRegular Price $11.99
EzGro Precision Micro TrimmerRegular Price $11.99 -
 Five Tower Deck GardenRegular Price $2,499.00
Five Tower Deck GardenRegular Price $2,499.00 -
 Submersible Thermoplastic Sump Pump 1/2 HPRegular Price $269.00
Submersible Thermoplastic Sump Pump 1/2 HPRegular Price $269.00 -
 Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 10 PackRegular Price $124.99
Drain Dish & Diffuser Dish Set 10 PackRegular Price $124.99 -
 Rainwater Pressure Tank SystemRegular Price $449.00
Rainwater Pressure Tank SystemRegular Price $449.00 -
 Chemilizer InjectorRegular Price $349.99
Chemilizer InjectorRegular Price $349.99









thank you :)